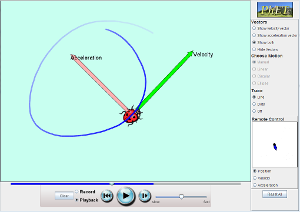
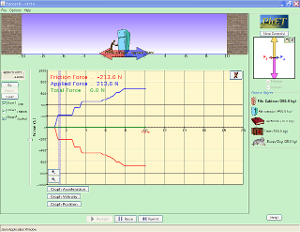
Kinematics (Review)
- Santa Claus's Crash Landing The old man has landed on the top of the roof of my house in Canada. Due to the large amount of ice on the roof, he starts to slide down the roof.Determine the vertical and horizontal speeds at which Santa Claus hits the ground using kinematic equations. (solution)
- Simulations
|
|
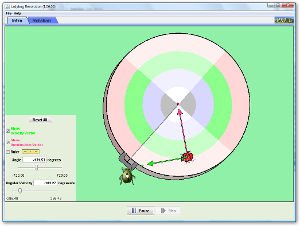 | Special Case: Uniform Circular Motion |
|
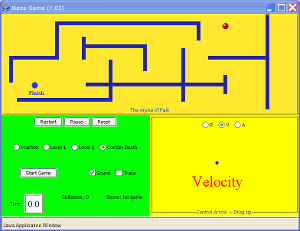 | Maze Game: Control ball by controlling r,v,a |
|
- Selected Problems.
- 3.38 Buried Treasure
- 4.59 Centrifuges
Dynamics
1. Key Relationships
Newton's 1st Law (define force: if no force, then no change in movement)
$$ { { \mathbf { \vec F }_{net} } = 0 \, \rightarrow \, \Delta \mathbf { \vec v}} = 0 $$
Newton's 2nd Law (how an unseen force results in visible acceleration → defn. of mass) $$ \mathbf { \vec a } = { { 1 \over m }{ \vec F }_{net}}$$
Combining Forces
$$ \mathbf { \vec F }_{net} = \sum \mathbf { \vec F }_{i} $$
2. Types of Forces
- Contact
- Spring Force (Push or Pull) (Fsp)
- Tension Force (Pull only) (T)
- Normal Force (n)
- Friction Force (f) -- opposite direction of motion
- drag (D) -- opposite direction of motion
- thrust (Fthrust)
- Long Range
- gravity
- electric
- magnetic
3. Free-Body Diagrams (including all the forces on an isolated body)
4. Forces in 1D (104-1 Lecture 6)
5. Drawing Free Body Force Diagrams: From different student perspectives